What is forming process?
Forming process is a cold forming operation standardly generated by hydraulic, mechanical and/or electromechanical forces.
What is Thread Rolling?
Thread rolling is a type of threading process which involves deforming a metal stock by rolling it through dies.
This process forms external threads along the surface of the metal stock. Internal threads can be formed using the same principle, specifically termed thread forming.
In contrast with other widely used threading processes such as thread cutting, thread rolling is not a subtractive process.
This means it does not remove metal from the stock.
The rolled threaded fasteners offer advantages such as stronger threads, precise final dimensions, good surface finish, and a lower coefficient of friction.
Which Threads can be realized by Thread Rolling Processes?
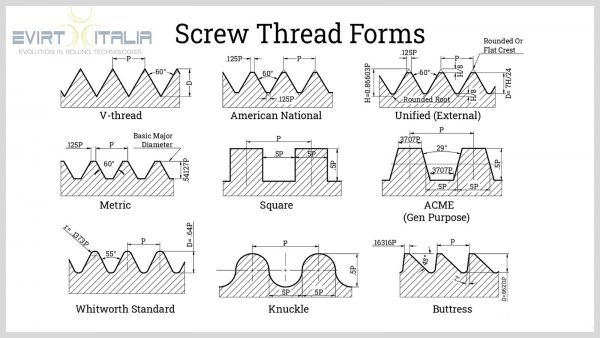
- V-Thread: triangular threads with flanks that typically form 60° with each other. The crests and roots are sharp, but in some cases, as a small flat portion due to limitations in fabrication.
- American National Thread: formerly known as the United States Standard Screw Thread, the American National Thread is a more standardized version of the V-thread which has specific dimensions to the flatness of the crests and roots of the threads.
- British Whitworth Thread: British counterpart of the American National Thread.
- Unified Thread: the thread form replaced the American National Thread along with thread standards from Canada and Britain. Developed to allow interchangeability of parts, Unified Threads still have the V-shape profile but with rounded or flat crests and roots. The Unified Thread Standard (UTS) consists of series, namely, Unified Fine (UNF), Unified Coarse (UNC), Unified Extra Fine (UNEF), and Unified Special (UNS).
- Metric Thread: developed to transition from the imperial-based measurement into the metric system. This was brought by the ISO, displacing the UTS thread form.
- Square Thread: special-purpose threads used for power transmission. Theoretically, they are the ideal thread for mechanisms and drive applications due to the perpendicularity of the load-bearing faces or flanks with the axis. However, this form is not practical due to manufacturing limitations.
- Acme Thread: the thread form is a variation of the square thread. The acme thread is characterized by having a trapezoidal form with a narrower root than its crest. Acme threads are stronger and easier to machine than square threads.
- Buttress Thread: in questo tipo di filettatura, un fianco è perpendicolare o leggermente inclinato rispetto all'asse mentre l'altro ha un angolo di 45°. Questa geometria del filetto è progettata per trasmettere carichi elevati in una direzione.
- Filettatura rotonda: in questo caso i filetti hanno creste e radici molto arrotondate con un angolo del fianco pari a 30°. Il profilo arrotondato consente di spostare i detriti per evitare la loro interferenza con l'ingranamento dei filetti.
- Tirante.
- Ingranaggio a vite senza fine.
- Profilo BSPT per collegamenti di tubazioni.
- Filettaure tonde.
- Dentature.
- Viti per il fissaggio delle rotaie.
- Zigrinature.
Which ones are the most used thread rolling methods?
What is the difference between thread rolling machine and thread cutting?
- The rolled thread is 30-40% more durable.
- The rolled thread surface is much stronger and smoother reducing as well the surface friction.
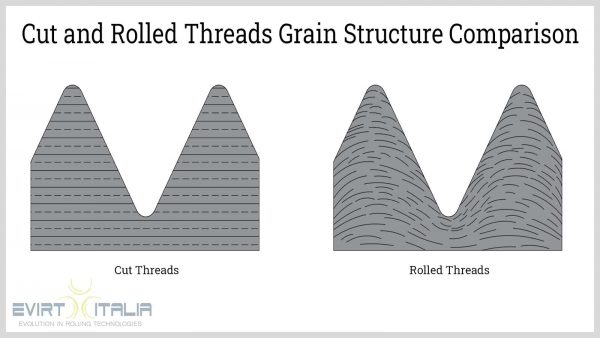
Thread rolling inherently imparts smooth and burnished threads without the need for secondary polishing processes. The high compressive forces that deform the metal remove any unevenness on the surface of the thread. Rolled surfaces have a surface roughness of approximately 8 to 24 microinches Ra while cut threads typically have 64 to 125 microinches Ra. - Rolling process is more suitable for threading materials that do not respond to heat treatment.
- The thread rolling dimensional accuracy is higher, indeed the dies used in thread rolling are mirror images of the threads to be generated and there is no material being removed from the stock, the process can produce parts with high precision and accuracy over long runs.
- The threading time is shorter compared to the machining method.
- The thread rolling process have a lower cost brought by the efficient use of material. This also leads to better energy utilization since there is no need to collect and recycle wasted materials.
- More delicate and compatible thread structure is obtained by thread rolling.
- In major sectors like goods, automotive, aerospace, construction, etc...) the thread formed by thread rolling method is preferred.
Which information are required to determine the capacity of the thread rolling machine?
9. Disegno tecnico del componente da produrre.
10. Flusso del processo produttivo.
11. Durezza del materiale.
Are thread rolling dies supplied together with the thread rolling machine?
With the aim to provide a complete key-hand solution, EVIRT ITALIA is standardly providing the tools together with machines.
What is in-feed process?
When the thread length is shorter than the die length, the type of rolling process is defined as infeed process.
During the infeed Thread Rolling process the workpiece is formed by a simple rotation while the workpiece is not moving backward or forward.
The in-feed rolling method is mandatory for those pieces which have a step in the front or behind the threaded section.
What is the meaning of Stud Bolt?
Stud bolt is a type of fasteners which present different lengths and fully threaded solid bars.
The Stud bolts were previously produced with standard thru-feed dies, while nowadays they can be produced faster and more precisely using the speed controlled thru feed dies thanks to the EVIRT ITALIA Smart Rolling Machines inclining heads.
Stud bolts are commonly used in construction, furniture and white goods industries.
EVIRT Mono & PlanWhat means 2 Die Cylindrical Thread Rolling Machinear Series?
The two dies cylindrical machines transmit the rolling force to material using two dies.
The two dies cylindrical thread rolling machines can produce a large variety of parts like splines, tie rods, etc. with the support of necessary equipment.
What means 3 die Cylindrical Rolling Machine - EVIRT Radial Series?
The three dies cylindrical Smart Rolling machines are the thread rolling machines whose pressure is conducted to the workpiece by three rolling dies.
The three dies cylindrical thread rolling machines can process hollow components or pipe similar shaped components.
What’s more, these series of machines are commonly used to roll different profiles on adjustment props as well as in scaffolding industries.
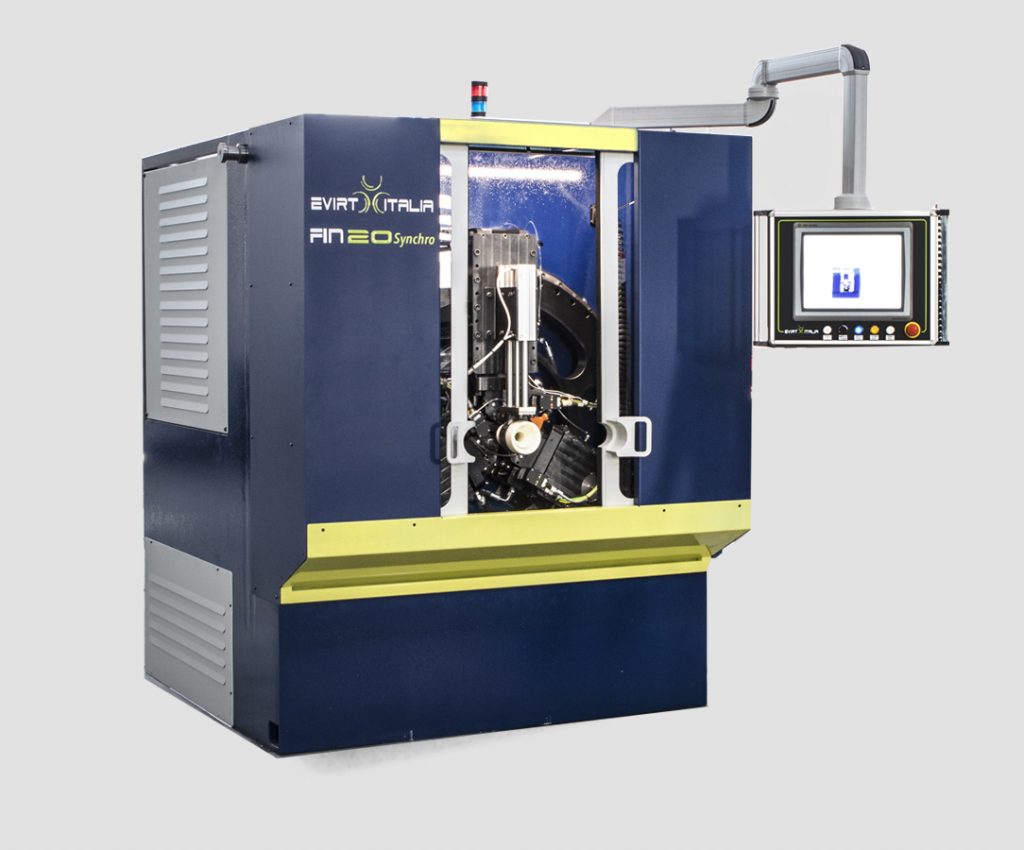
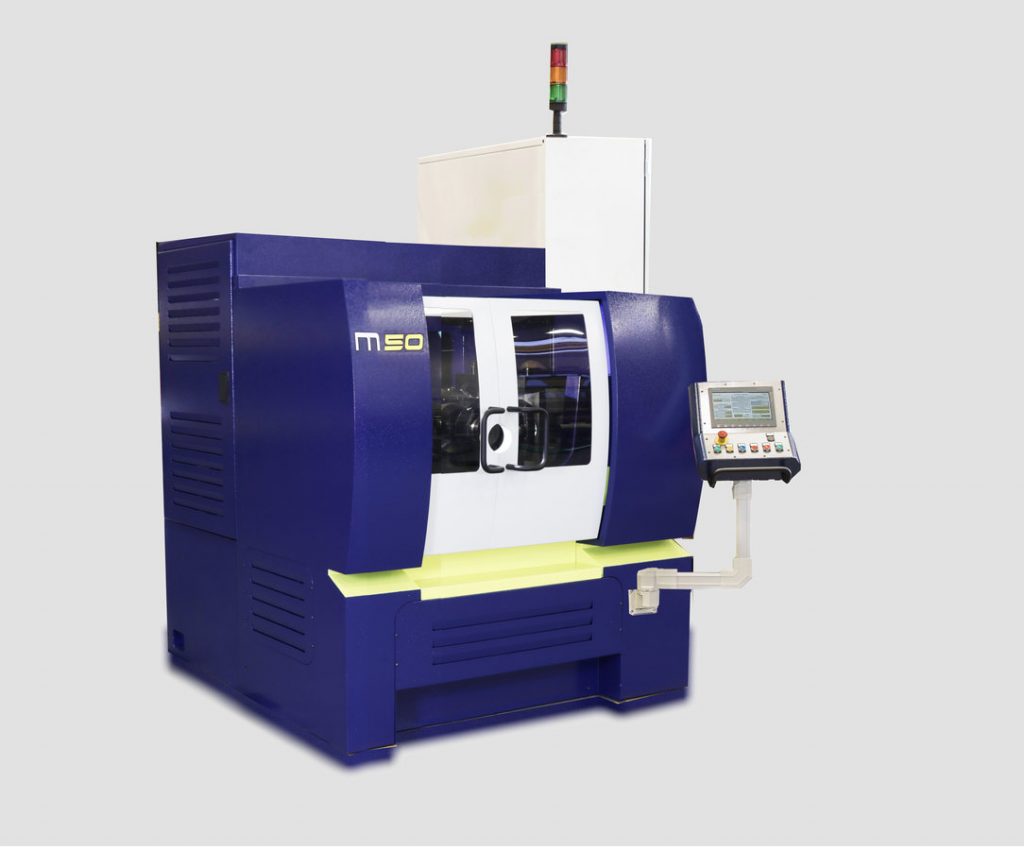
What is the Thread Rolling Machine?
The Thread Rolling Machine is a machine that can cold form circular cross sectioned materials like threads, knurls, splines, tie rods can be formed.
These machines performs faster and better products than cutting machining.
By rolling the material, the molecular structure of the material is oriented, causing a durable product with increased quality.
What is the Thread Rolling Die?
The thread rolling dies are as the tools used on the thread rolling machines.
Thread rolling dies material type is chosen according to workpiece material.
What is the life of Thread Rolling Die?
What is the meaning of Speed control thru-feed dies?
Speed controlled thru-feed dies are used for threads longer than die length using inclined spindles.
These kinds of dies are also able to perform faster process than rolling through-feed dies.
Another difference compared with through-feed dies is the absence of connection between dies shape and thread shape.
Watching at the profile, the main difference is the fact that dies present grooves on thread cross section instead of helical thread.
Using ring dies make available faster thread rolling production.
What is the meaning of Ball Joint?
All vehicles steering and front alignment systems requires mobile cardan parts which are called Ball joint (ball pin).
It exists an enormous kind of types, shapes and sizes related with vehicle brand and vehicle's system.
These parts are forged with multiple station cold forging machines, then machined with lathes and finally the ball side of part is burnished and straightened by rolling machines.
In last decades EVIRT ITALIA developed special purpose machines for burnishing and rolling operation on ball joints in order to maximize their operation efficiency.
What is the difference between Single ended or Double ended studs?
The single ended studs are threaded on one single side while the double ended studs are rolled on both sides of the bolts.
EVIRT ITALIA innovative double station thread rolling machines made the double studs rolling process simple and intuitive like never before.
What is the meaning of cold forming processes?
Cold forming processes are shape deformation processes which exceed the plastic limits of material deformation by using a certain amount of rolling force.
The structure of the material obtained as a result of cold forming, unlike the state before the rolling process, is in the direction of the thread rolling force application.
This oriented structure is then much more durable and harder than its original state.
As a consequence of this process, as much as the cold forming force increases, the depth and stiffness of the resistant structure increases at the same rate.
What is the meaning of Spline Rolling Process?
Spline Rolling Process is a kind of fastener process which needs both high torque and high rolling force.
The splines can be produces by EVIRT ITALIA Smart Rolling Machines which are able to thread up 1.95 module with reference DIN 5480 standard.
What is the definition of Tie Rod?
Tie Rod is a material which has a special profile.
It’s normally produced to be used in the construction sector, in mold binding as well as in anchoring operations.
Tie Rod can be produced using EVIRT ITALIA Smart Rolling Machines.
Tie Rod is mostly produced with the following diameters: Ø 17, Ø 22, Ø 24, Ø 27 and Ø 32 mm.
Which ones are Common Defects of Thread Rolling Processes:
Though the thread rolling process offers higher precision than others, upsets and irregularities in the operation will inevitably create defects.
Most of the defects arise from the out-of-tolerance stock dimensions, worn-out or misaligned rollers, and improper stock feeding.
Below are the most common defects seen in thread rolling.
- Truncated Thread Crest:
This defect is described by a non-fully formed crest or an excessively truncated crest.
One reason could be an undersized stock where there is insufficient material to flow and create the crests.
This is fixed by gradually increasing the size of the stock. If the pitch diameter is oversized, then the more probable root cause is a loose threading head which is solved by sizing-in.
If not, then the defect is possibly caused by too much hardness of the material.
Thus, it is then necessary to change into a softer material.
- Flaking:
Flaking or slivers causes unusual roughness on the surface of the threads.
This is usually caused by the incompatibility of the material for rolling.
The root causes can be excessive lead and sulfur content, inconsistent grain structure, and sometimes cold working before rolling.
If the material being used already has a good rollability, then other possible causes can be mismatched rollers or dies, rough roller surface, overfilling, or slow rolling speeds.
- Drunken Threads:
This defect is seen as wavy or uneven thread crests.
This is a result of mismatched dies, misaligned feeding of the stock, or poor die construction.
The best solution is to check the condition of the rolls and their bushings.
- Curved Pitch Line:
This is viewed as the tapering of the threads towards the ends of the threaded segments of the bolt or screw.
The curvature can be concave or convex.
Its root causes are inconsistent stock diameter, misaligned stock relative to the roller, wearing of rollers, or too much deformation of the material causing it to flow towards the end of the stock.
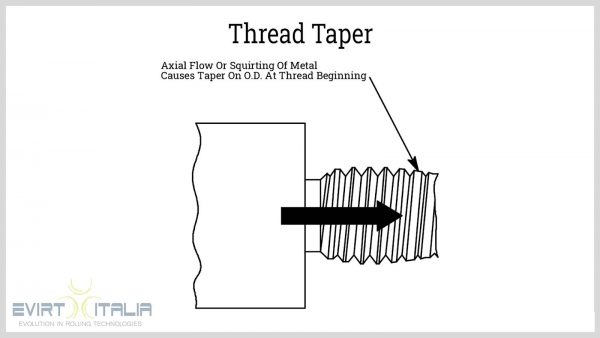
- Out-of-tolerance Helix Angle:
This can be a result of a variety of causes such as unsynchronized rollers, imperfect rollers, incorrect feeding of the stock, or screw jacking.
This can be solved by correctly timing and aligning the rollers, proper stock feeding, and optimizing the rolling speed.
- Poor Finish:
Poor finish is a result of factors such as worn-out dies, high material hardness, oversized stock diameter, or presence of contaminants in the coolant supply.
- Cupped End:
A cupped end appears as a concave-end caused by forcing the metal to flow over an insufficient chamfer.
This is more evident on softer metals.
The defect is solved by properly chamfering the stock, usually about 30°.

Which ones are the most famous thread Rolling Machines?
Thread rolling process summary is true to any type of thread rolling.
There are different types of thread rolling machines that vary according to the type of die used.
Thread rolling machines can be a flat-die, planetary, or cylindrical-die type.
- Flat-die Type:
• this type of thread rolling machine consists of two rectangular dies where one is stationary while the other is reciprocating.
The reciprocating die moves parallel to the stationary die.
The surface of the dies contains ridges representing the profile of the thread to be produced.
These ridges are inclined at an angle equal to the helix angle of the thread.
The distance between the crests of the dies is equal to the minor diameter of the thread.
The threads are formed typically in one passage only.
The length of the die allows the stock to be rolled around six to eight times.
The stock is inserted on one end, either manually or automatically.
The dies roll the stock tangentially which carries it up to the opposite end by friction.
- Segment or Planetary Type:
A planetary type operates by rolling the stock through one stationary and one moving surface.
However, this machine uses rotating motion instead of translation.
This type involves stationary curved dies and a central rotating die.
One or more stationary dies can be matched with a single rotating die. A stationary die rolls one stock at a time.
Similar to the flat-die type, the planetary machine has a finite rolling surface that forms the thread through one passage.
The stock is inserted on one end of the curved die.
The rotating die then rotates a full arc of the curved die revolving the stock until ejected on the opposite end.

- Cylindrical-die Type:
Cylindrical dies or rollers are regarded as dies with infinite work surfaces.
These machines, for which EVIRT ITALIA is the most trustable brand in the world, are usually operate through the combination of radial and through feeding.
Unlike the flat-die and planetary types, the cylindrical-die type deforms the metal through multiple passes as it rolls.
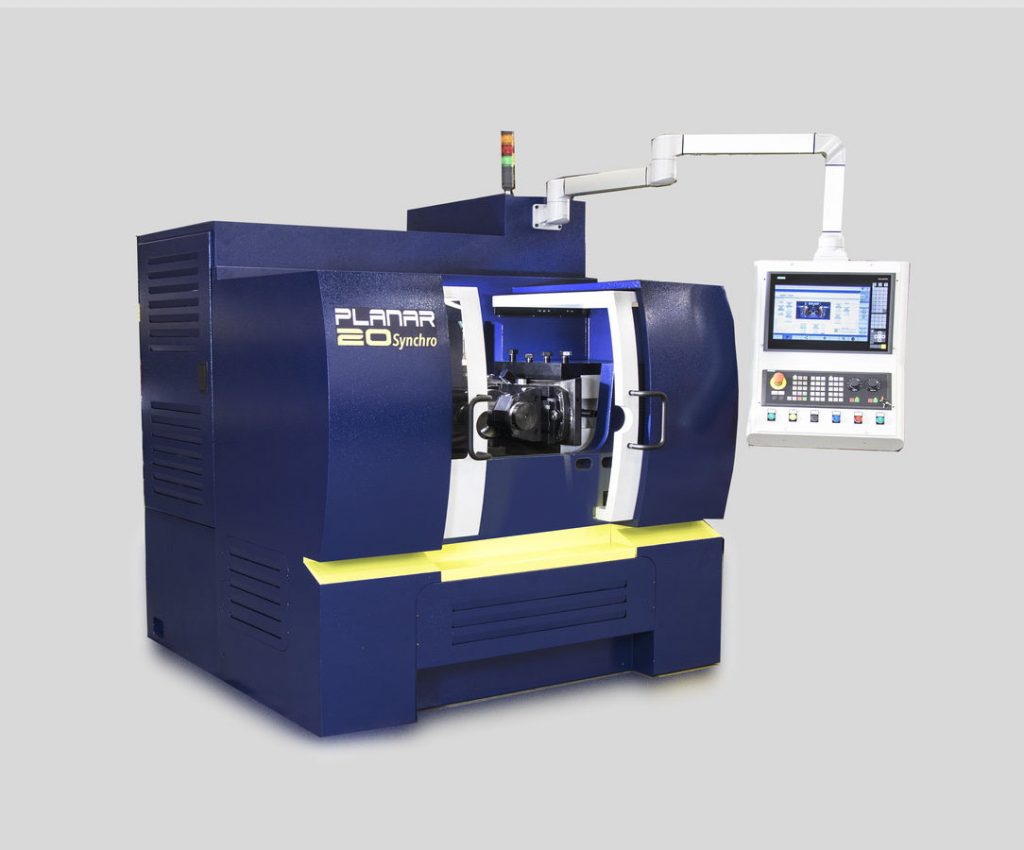
Cylindrical-die type machines can be further divided into two major categories: two-die (Planar series) and three-die machines (Radial series).
- Two-die (serie Planar):
This type of threading machine has two parallel rollers wherein one or both can move radially to accept and penetrate the stock.
The stock is positioned with a slight offset from the plane of the centerline of the dies to prevent it from rising out.
A smooth roller support or rest bar is located in the middle to hold the stock as it is being threaded.
- Three-die (serie Radia):
This machine has three rollers positioned 120° from each other.
Typically, all rollers can move radially wherein the position of the stock is maintained at the center during penetration.
Compared with two-die machines, three-die types have better force balance but are more difficult and complex to adjust.











